How to operate a drone: Unlocking the skies opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate data collection. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to safely and effectively pilot your drone, covering everything from essential regulations and pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques and responsible drone operation. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone components, explore various flight maneuvers, and offer valuable insights into drone maintenance and troubleshooting.
Prepare for takeoff!
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide breaks down the complexities into manageable steps, allowing both beginners and experienced users to enhance their skills. We emphasize the importance of adhering to safety regulations and ethical considerations throughout the process, ensuring a responsible and enjoyable flying experience.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and prioritizing safety. This section covers essential aspects of safe drone operation, from licensing requirements to pre-flight checks and emergency procedures.
Drone Licensing and Permits
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. In many regions, operators are categorized based on drone weight, intended use (recreational vs. commercial), and flight location (e.g., near airports). Some countries require registration of the drone itself, while others mandate operator licensing or permits, often involving online examinations and practical assessments. For example, the United States utilizes a system of registration and certifications through the FAA, differentiating between recreational and commercial drone operation.
The European Union has implemented a similar system with varying levels of certification based on the drone’s weight and intended use. Always check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations in your area.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a systematic approach encompassing pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight procedures. These procedures minimize risks and ensure both the drone and surrounding environment remain safe.
- Pre-flight: Conduct thorough pre-flight checks, including battery level, GPS signal strength, and visual inspection of the drone’s components. Check weather conditions and ensure airspace is clear.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoid flying near obstacles or people, and be aware of surrounding airspace. Be prepared to land immediately if necessary.
- Post-flight: Secure the drone properly, recharge the batteries, and review flight logs to identify any potential issues.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist helps ensure safe and efficient operation. This checklist is not exhaustive, and additional checks may be required depending on the specific drone model and operational context.
- Check battery level and condition
- Inspect propellers for damage
- Verify GPS signal lock
- Check for software updates
- Confirm proper calibration of sensors
- Review weather conditions and airspace restrictions
- Inspect camera functionality (if applicable)
Drone Safety Features Comparison
Various drone models incorporate safety features designed to enhance flight stability and prevent accidents. These features contribute to safer operation, particularly for novice pilots.
| Feature | Description | Importance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point | Prevents loss of drone in case of signal loss or low battery | Most modern drones include this feature. |
| GPS Fail-Safe | Initiates a safe landing procedure if GPS signal is lost | Ensures a safe landing in areas with weak or no GPS signal | Some drones will attempt to maintain position using other sensors if GPS is lost. |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles | Minimizes risk of collisions with objects | Many drones offer ultrasonic or vision-based obstacle avoidance. |
| Geofencing | Limits the drone’s flight range to a predefined area | Prevents accidental flights into restricted airspace | This is often set by the drone’s software or app. |
Understanding Drone Components
A drone is a complex system composed of several interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in its flight and functionality. Understanding these components is essential for effective operation and troubleshooting.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions
The core components of a typical drone include the frame, motors, propellers, flight controller, battery, GPS module, and camera (for aerial photography/videography). Each component contributes to the overall functionality of the drone.
- Frame: Provides structural support for all other components.
- Motors: Provide the propulsion for the drone.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for flight.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, controlling the motors and other systems.
- Battery: Powers the drone.
- GPS Module: Provides positioning information.
- Camera: Captures images and videos (optional).
The Flight Controller’s Role
The flight controller is the central processing unit of a drone, responsible for coordinating the actions of all other components. It receives input from various sensors (e.g., gyroscope, accelerometer, barometer, GPS) and uses this data to adjust the speed and direction of the motors, maintaining stability and executing flight commands.
Drone Batteries and Charging
Drone batteries are typically lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries. They require specific charging procedures to ensure safety and longevity. Always use the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Overcharging or discharging LiPo batteries can be dangerous.
Drone Propulsion System Diagram
The drone’s propulsion system comprises the motors, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), and propellers. The ESCs receive signals from the flight controller and regulate the power supplied to the motors, enabling precise control of the drone’s movement. A visual representation would show the ESCs connected to each motor, which in turn are attached to the propellers. The flight controller sends signals to the ESCs, and the propellers generate thrust based on these signals.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Procedures
Before each flight, careful preparation is crucial to ensure a safe and successful operation. This involves a series of checks and calibrations to guarantee optimal performance and minimize potential risks.
Drone Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors is essential for accurate flight control. This usually involves a series of steps performed through the drone’s control app or software. The specific steps may vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve leveling the drone and following the on-screen prompts.
Weather and Airspace Checks
Before takeoff, always check weather conditions and airspace restrictions. Strong winds, rain, or snow can significantly impact drone stability and control. Flying in restricted airspace, such as near airports or military installations, can lead to legal consequences and safety hazards.
Essential Tools and Equipment
Having the right tools and equipment ensures efficient drone operation and maintenance. This includes spare batteries, propellers, a charger, and potentially specialized tools for repairs.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively maneuver your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This site offers comprehensive guidance on everything from basic flight techniques to more advanced maneuvers, ensuring you can confidently handle your drone.
Proper drone operation requires practice and a commitment to safety regulations.
- Spare batteries
- Spare propellers
- Battery charger
- Screwdrivers
- Calibration tools (may vary by drone)
Pre-Flight Setup Checklist
A pre-flight checklist is vital to ensure that all systems are ready before initiating flight. This structured approach minimizes the risk of overlooking crucial steps.
- Charge batteries to full capacity
- Inspect drone for any physical damage
- Verify GPS signal acquisition
- Check for and install any software updates
- Calibrate sensors according to manufacturer instructions
- Review weather conditions and airspace restrictions
- Power on drone and controller
Basic Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic drone flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers the essential controls and maneuvers necessary for initial flights.
Basic Flight Controls

Most drones utilize four basic controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. These controls manipulate the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls movement left and right (sideways).
Flight Maneuvers
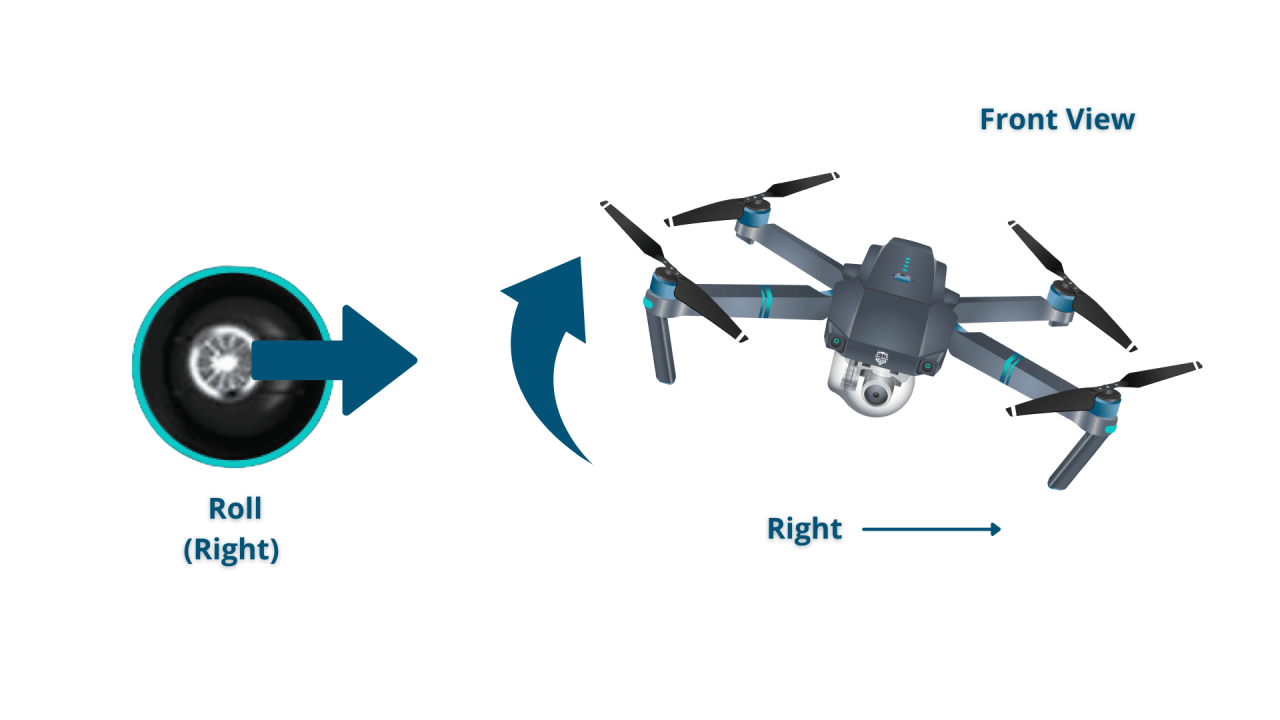
Basic flight maneuvers include hovering, ascending, descending, and turning. Mastering these is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers.
Differences in Flight Controls
Flight control interfaces can vary slightly between drone models. Some drones may use different stick configurations or button layouts, requiring familiarity with the specific model’s controls.
Common Flight Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial for safe drone operation. These mistakes can range from simple errors to more serious issues that could result in accidents.
- Not checking battery level before flight
- Ignoring weather conditions
- Flying too close to obstacles
- Losing visual line of sight
- Failing to follow airspace regulations
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone

Beyond basic flight, advanced techniques enhance drone capabilities for more complex operations. These techniques require practice and a thorough understanding of drone systems.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. This is useful for tasks requiring precise movements or repetitive patterns.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from controls to safety protocols. Successfully operating a drone requires practice and adherence to these guidelines for safe and efficient flights.
GPS and Sensor Utilization
GPS and other sensors (IMU, barometer) provide precise positioning and stability. Advanced flight modes often rely heavily on these sensors for accurate control.
Complex Drone Flight Mission Planning
Planning a complex mission involves careful consideration of factors such as flight path, altitude, speed, and potential obstacles. Specialized software can aid in this process.
Using Drone Flight Planning Software
Software like DJI GO 4 or Litchi allows for advanced flight planning, including setting waypoints, adjusting camera settings, and simulating flights. These programs offer a user-friendly interface for creating complex flight paths.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques is key to achieving high-quality results.
Adjusting Drone Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture directly affect image quality. Optimizing these settings based on lighting conditions is crucial for sharp, well-exposed images and videos.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving high-quality aerial media involves understanding composition, lighting, and movement. Smooth, controlled movements are essential for professional-looking footage.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles and perspectives can dramatically change the mood and impact of aerial shots. Experimenting with various angles is key to creative storytelling.
Drone Camera Features Comparison
Different drone cameras offer varying features and capabilities. Understanding these differences helps choose the right drone for specific needs.
| Feature | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Image sensor size and pixel count | Higher resolution produces sharper images and videos | Higher resolution files require more storage space |
| Field of View (FOV) | The angle of view captured by the lens | Wider FOV captures more of the scene | Wider FOV can lead to distortion at the edges |
| Image Stabilization | Techniques used to reduce camera shake | Produces smoother videos and sharper images | Can slightly reduce image quality |
| Video Frame Rate | Number of frames per second | Higher frame rates enable smoother slow-motion playback | Higher frame rates require more storage space |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for keeping a drone in optimal working condition and extending its lifespan.
Regular Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance involves inspecting the drone for damage, cleaning propellers and the camera lens, and checking all connections.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Common drone problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor malfunctions. Understanding the causes and solutions for these issues is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect the drone from damage. Use a protective case or bag and avoid exposing the drone to extreme temperatures or moisture.
Common Drone Parts and Replacement, How to operate a drone
Knowing how to replace common drone parts, such as propellers, batteries, and motors, enables quick repairs and minimizes downtime.
Drone Laws and Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation involves adhering to all applicable laws and ethical guidelines. This ensures safety and respects the rights and privacy of others.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Drone laws vary by location and often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational guidelines. Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive surveillance, and being mindful of potential risks.
Respecting Privacy and Avoiding Intrusive Surveillance
It is crucial to respect the privacy of individuals and avoid capturing images or videos without their consent. Drone operation should always be conducted responsibly and ethically.
Potential Risks and Responsibilities
Drone operation carries inherent risks, including accidents, property damage, and legal consequences. Operators are responsible for their actions and the safe operation of their drones.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Use
Responsible drone use involves adhering to all applicable laws and regulations, respecting the privacy of others, and operating the drone safely and responsibly.
- Obtain necessary licenses and permits
- Check weather conditions and airspace restrictions before each flight
- Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times
- Avoid flying near people or property
- Respect the privacy of others
Successfully operating a drone involves a commitment to safety, continuous learning, and responsible piloting. By understanding drone regulations, mastering flight controls, and embracing ethical considerations, you can unlock the full potential of this remarkable technology. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect airspace restrictions, and appreciate the breathtaking perspectives that drone operation offers. Happy flying!
FAQ Overview
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners, prioritizing ease of use and safety features. Research models known for their intuitive controls and stability.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, weather conditions, and flight style. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, prioritize safety. Attempt to regain control using emergency procedures (if applicable to your drone model). If unsuccessful, land it in a safe location, away from people and property.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone flight is heavily regulated. Always check local laws, airspace restrictions, and no-fly zones before each flight using approved apps like B4UFLY or similar.
